Polyethylene CNC PE Machined Parts Plastic Part
Mainstream Processing Technologies and Typical HDPE Part Types
Injection Molding (Large-Scale Standardized Parts)
Process Features: HDPE granules are heated to a molten state (180-240°C), injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, and then cooled and solidified. This process is suitable for producing small and medium-sized parts with complex structures and large production runs (≥10,000 pieces).
Typical Parts:
Food/Medical Industry: Injection-molded HDPE measuring cups (such as laboratory measuring instruments), medicine bottle caps (FDA-compliant), and syringe plunger covers (with high biocompatibility requirements).
Industrial Accessories: Plastic gears (for low-speed transmissions), dust covers (such as motor end caps), and cushioning blocks (for shock absorption).
Advantages: High efficiency (cycle times of a few seconds to a few minutes per part), high surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.4 μm), and the ability to integrate inserts (such as metal shafts).
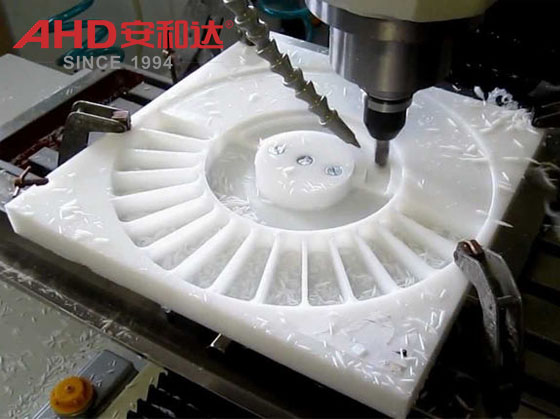
CNC Machining (High-Precision Customized Parts)
Process Features: HDPE rods and sheets are machined using CNC lathes, milling machines, drilling machines, and other equipment. This process is suitable for small batches (≤1,000 pieces), high precision (±0.05 mm), and complex shapes (such as irregular holes and curved surfaces).
Typical Parts:
Mechanical Industry: HDPE guide rails and sliders (self-lubricating metal alternatives), bearing seats (lightweight design), and equipment protective covers (corrosion protection).
Chemical Industry: Corrosion-resistant pipe joints (such as acid and alkali liquid transportation), reactor agitator blades (wear resistance), and valve seals (chemical resistance).
Electronics Industry: Insulation brackets (such as circuit board supports) and high-frequency signal shielding covers (low dielectric loss). Key Processes: Cutting parameters must be controlled (speed 500-2000 rpm, feed rate 0.05-0.2 mm/r) to avoid work hardening or overheating deformation. The surface can be polished (Ra ≤ 0.2 μm) or sandblasted (to enhance slip resistance).
Extrusion Molding (Long/Tubular Parts)
Process Features: HDPE granules are heated and melted in a screw extruder, then continuously extruded through a die into pipes, rods, or profiles. These are then cut or processed into the desired components. This process is suitable for long (e.g., pipes ≥ 10 m) linear parts with consistent cross-sections.
Typical Parts:
Pipes: HDPE chemical pipes (acid and alkali resistant), laboratory gas hoses (non-toxic and odorless), agricultural irrigation pipes (UV resistant).
Profiles: Equipment frames (e.g., lightweight workbenches), sealing strips (e.g., waterproof edges for doors and windows).
Advantages: Low continuous production costs, and the ability to customize complex cross-sections (e.g., multi-lumen pipes and ribbed structures).
Specialty Processing (Functional Upgrade)
Thermoforming: HDPE sheets are heated and softened, then vacuum-formed/pressure-formed to create large, thin-walled components (such as radiator caps and trays).
3D Printing Adaptation: Using FDM (fused deposition modeling) technology, HDPE filament (particle size ≤50 μm) is used to print customized parts (such as prototype verification parts and small fixtures). However, the surface roughness is relatively high (Ra ≥ 1.6 μm), requiring subsequent polishing.
Surface Modification: Functional upgrades can be achieved through plasma treatment (to enhance adhesion), application of wear-resistant coatings (such as PTFE coatings for increased friction resistance), and the addition of antistatic agents (surface resistance ≤ 10⁹ Ω).
Typical Applications
- Chemical Equipment: HDPE acid tank linings (resistant to sulfuric and hydrochloric acids), reactor agitators (resistant to chlorine and alkali corrosion), and pipe elbows (resistant to wear), with a service life of over 10 years (compared to the 3-5 years for ordinary metal parts).
- Wastewater Treatment: Corrosion-resistant HDPE gratings (for sewage tank covers) and ventilation duct connectors (resistant to biogas corrosion) replace stainless steel and reduce maintenance costs.
- Food Processing: FDA-compliant HDPE cutting boards (antibacterial and easy to clean), baking molds (resistant to high-temperature steam sterilization), and conveyor rollers (food-safe).
- Medical Devices: Medical-grade HDPE surgical instrument trays (easy to sterilize), syringe accessories (biocompatible), and laboratory equipment (such as Petri dish holders).
- Mechanical Transmission: Self-lubricating HDPE gears (low-speed transmission), bearing bushings (replacing bronze bearings), and guide rails (reducing noise and wear).
- Equipment Protection: Corrosion-resistant HDPE operating panels (resistant to chemical splashes) and safety fencing (lightweight and impact-resistant).
- Building components: HDPE drainage pipes (resistant to freeze-thaw cycles), balcony railings (lightweight and rust-resistant), and landscape sculpture supports (excellent weather resistance).
- Household items: Non-toxic and odorless HDPE children's toys (such as building blocks), cosmetic storage boxes (easy to clean), and high-end furniture mats (anti-slip and shock-absorbing).